Cervical osteochondrosis is a progressive degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the intervertebral discs located between the first 7 vertebrae. Vertebrae 1-7 belong to the cervical spine.
Pathological changes against the background of osteochondrosis lead to deformation of the vertebrae, which ultimately disrupts their blood supply, nerve conduction in the neck and areas of innervation of damaged nerves.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be an independent disease or combined with osteochondrosis of other parts - thoracic and lumbar.
Main symptoms
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain, the localization and nature of which depends on the location of the lesion. It is most often felt in the neck area, on one or both arms.
This disease is characterized by unilateral pain, and any part of the arm can hurt - the shoulder, the forearm, the hand and even the fingers. Many patients complain of headaches and dizziness.
The pain syndrome can also be felt in the chest, in the supraclavicular region or spread throughout the back. For some, the pain is centered at the base of the neck or throat.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is characterized by a number of symptoms and is often accompanied by a disorder of tactile sensitivity, muscle weakness, decreased visual acuity and hearing, rapid heartbeat and panic attacks.
Careful! Sometimes osteochondrosis is complicated by vertebral artery syndrome, which may require urgent hospitalization of the patient.
The first signs
In the early stages, the manifestations of osteochondrosis are more reminiscent of the usual fatigue after a busy day and occur periodically. In the evening, discomfort and pain in the neck, heaviness and pain in the head appear, mainly in the occipital region. Possible crackle and crackle when turning the head.
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis in women are more pronounced than in men and are often associated with an unstable psycho-emotional state. In addition, men suffer from this disease much less often.
Aggravation of chondrosis often occurs during menopause, when hormonal changes occur in the female body and the immune system weakens. Some difficulties arise with the diagnosis because of the signs similar to those of many other diseases.
The severity of the symptoms depends on the stage of the disease, the nature and degree of damage to the spine
Men react less to small things like a crack in the neck and often simply do not notice suspicious symptoms. In addition, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men may not appear for a long time, which is explained by the peculiarities of anatomy.
Men have naturally more developed and stronger muscles, which creates additional support for the spine. The muscular framework serves as a kind of armor that protects the vertebrae and prevents their deformation.
Vertebral artery syndrome (VAS)
The clinical picture of SPA is usually represented by several symptoms, but only one of the possible ones can be observed:
- headache with a predominant localization in the back of the head and at the base of the skull - basilar migraine, accompanied by classic symptoms: loss of coordination, nausea leading to vomiting, tinnitus, less often - speech impairment;
- dizziness that occurs when turning the head. They can be accompanied by vomiting, darkening of the eyes and impaired coordination of movements;
- eye fatigue from stress, flickering of the spots and bright flashes before the eyes and in some places loss of visual fields. Patients may complain of pain, redness and feeling of sand in the eyeballs, inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- constant or episodic tinnitus, the nature of which varies depending on the position of the neck. There may be mild deafness, ear blockage, and unresponsiveness to a quiet voice. In some cases, paracusis was observed - selective hearing of sounds, in which a person hears better in the presence of external noise than in complete silence;
- vegetative symptoms always appear when osteochondrosis worsens, and are most often combined with other symptoms. These can be hot flashes or chills, increased sweating, cold feet and hands, a feeling of shortness of breath, increased blood pressure and poor sleep;
- TIA - transient ischemic attacks - accompany mechanical pinching of the vertebral artery and are manifested by double vision, temporary partial blindness with loss of visual fields, dizziness with vomiting, speech and swallowing disorders;
- Fainting can be a consequence of sudden turns of the head or its uncomfortable position. The loss of consciousness lasts for different periods of time and leaves weakness in the limbs;
- drop attacks are sudden falls, usually without loss of consciousness, caused by a sudden rush of blood to the brain when the head is thrown back. The immediate cause is paralysis of the legs, but motor function is restored fairly quickly.
Headache and dizziness
Most patients with cervical chondrosis have this symptom, but it may be absent. The cause of dizziness is associated with the compression of the main arteries and blood vessels, which prevents the transport of oxygen to the nerve tissue of the medulla oblongata and the spinal cord.
Under the influence of mechanical trauma of the vertebral structures and chronic ischemia of nerve fibers, sensitivity increases and irritation of nerve endings occurs, which ultimately causes cervical vertigo.

A headache caused by chondrosis can be distinguished by its location in the back of the head. However, there are also not quite typical cases when the whole head or one side of it hurts
Dizziness can be accompanied by uncertainty of movements, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure and increased sweating in the area of the face and shoulders.
Headache is a frequent accompaniment of cervical chondrosis. It has a paroxysmal nature, the duration of the attack varies from several hours to several days. The intensity of the pain varies, but appears with enviable regularity.
The headache is caused by compression of the vertebral artery due to changes in the position of the vertebrae and discs. Due to the compression of the vessel, the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, which leads to pain.
Reference:
The cause of pain can also be muscle spasm, typical for osteochondrosis.
Panic attacks
Panic attacks are also associated with a reduction in brain nutrition and cause the following symptoms:
- attacks of fever or chills, increased body temperature;
- numbness, tingling in the limbs, muscle spasms, impaired motor skills;
- dizziness, loss of coordination, darkening of the eyes;
- pain behind the sternum or in the chest on the left, rapid pulse, increased blood pressure;
- insomnia, fear of death or mental confusion, confusion;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing up to suffocation, lump in the throat;
- discomfort and pain in the abdomen, indigestion, frequent urination.
Sore throat
The throat with osteochondrosis hurts, as a rule, when the 4th cervical vertebra is damaged or displaced. The localization is usually unilateral, as the vertebrae and discs are displaced to one side.
Sore throat is caused by damaged innervation of pharyngeal muscles due to nerve compression
Due to the tightening of the roots, spasm and tension of the muscles of the pharynx occur, accompanied by pain. The throat feels heavy and full, and it becomes difficult to breathe. However, there are no mechanical obstacles to free breathing and swallowing; there are no foreign objects or tumors in the esophagus and larynx.
It is typical that medications for tonsils or sore throats, gargling and inhaling do not work.
The source of the pain is in the area between the thyroid cartilage and the jugular cavity. The nature of the pain ranges from mild to debilitating.
Treatment
Complex treatment of cervical osteochondrosis includes several methods - taking medications, performing therapeutic exercises, attending physiotherapy and massage sessions. If you wish, you can use folk remedies and make various compresses, prepare infusions and decoctions.
In case of worsening of the disease, it is recommended to adhere to bed rest. In addition, you need to lie on a flat and fairly firm, elastic surface - a hanging sofa or feather bed will not work.
Careful! Severe pain requires immediate medical attention.
To adjust the cervical spine, the doctor may prescribe wearing a Shants collar. It supports the neck in an anatomically correct position, eliminating movements and therefore pain.
Medicines are chosen taking into account existing symptoms and diagnostic results. If hernias and protrusions are detected, the treatment may be surgical.
| dope | action |
| Active ingredient: Pentoxifylline | Improves cerebral circulation, expands blood vessels, relaxes smooth muscles, reduces the frequency of nerve signals |
| Preparations with chondroitin and glucosamine | Restoration of the cartilaginous tissue of the discs, slowing down the degenerative processes |
| Muscle relaxants | Relief of muscle spasms |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Relief of the inflammatory process, tissue swelling |
| Analgesics | Pain relief |
| opioid | For severe pain that cannot be relieved by conventional means |
| Vitamin complexes containing vitamins B, A, C, calcium | Strengthening of nervous, muscular and bone tissues, general healing effect |
| Antidepressants and tranquilizers | Coping with stress caused by constant pain |
Treatment at home
It is not recommended to stay at home for too long and follow bed rest, and after the acute symptoms disappear, you should switch to active actions. You should start with simple exercises and gradually move to more intense ones.
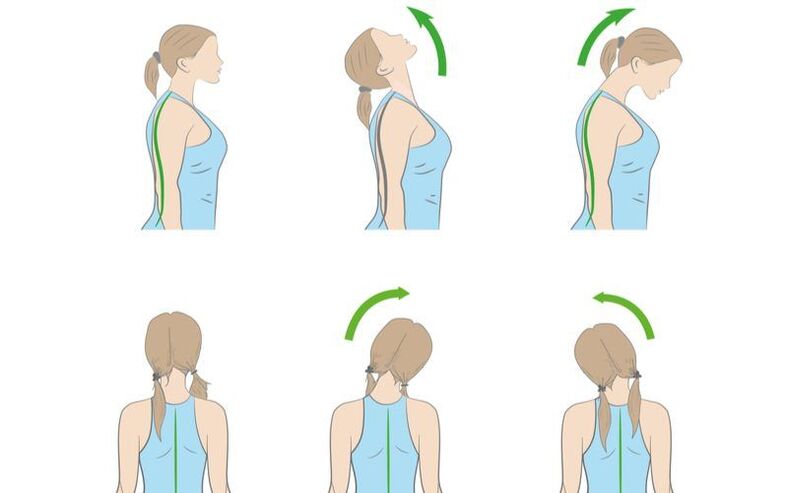
Performing neck exercises helps strengthen the neck muscles, thus preventing the recurrence of irritations
Exercise 1 - self-extension. Standing with your arms down along your body, tilt your head to the right and at the same time reach down with your left hand. Stay in this position and repeat the exercise on the other side.
Exercise 2 - self-massage. Put the towel on your shoulders and, holding its ends, pull it in one direction or the other.
Exercise 3 – turning the head left and right, tilting to the right and then to the left shoulder.
Exercise 4 - the same with counteraction with your hand: when you turn or lean, press on your temple, creating additional resistance.
Tips for preventing osteochondrosis
Tip #1
Physical education is the main way to fight the aging of the body and the development of intervertebral disc dystrophy. Daily exercise and a visit to the pool at least once a week are usually enough. All this allows you to strengthen the muscular corset of the spine.
Tip #2
Even a healthy person needs massage sessions; it is recommended to do them every year.
Tip #3
It is very important to monitor your weight and avoid gaining extra pounds.
Tip #4
When you work in a forced position for a long time, you should take breaks, change your body position and do a warm-up.
Tip #5
Eating well means consuming enough vitamins and trace elements with food.
Tip number 6
Try not to lift or carry heavy objects, and if you must, wear a support brace.
FAQ
When should you go to the doctor urgently?
Reasons for immediate consultation and even calling an ambulance are:
- persistent numbness of the arms or legs;
- severe pain that is not relieved by conventional analgesics;
- movement disorder;
- severe headache, dizziness, loss of coordination and other signs of cerebrovascular accident;
- "Locking" the back in a certain position, severely limiting movements.
Is it possible to cure chondrosis forever?
No, this is a chronic disease with periodic flare-ups. Even after treatment and following all the doctor's recommendations, the cartilage in the affected area of the disc is replaced by scar tissue. This means, the structure of the segment is already damaged, and this process is irreversible. However, with some effort on the part of the patient, a high quality of life can be achieved.